Flexible X-ray Shielding Material with Novel Coaxial Fiber Design Outperforms Traditional Lead-Based Options
A breakthrough in flexible X-ray shielding materials has been achieved through the innovative use of a coaxial fiber structure. Researchers have successfully developed a high-performance, paper-like material based on aramid nanofiber (ANF) and perovskite CsPbBr3, offering superior protection, flexibility, and lightness compared to conventional rigid shields.
Key Innovation: In-Situ Synthesis within a “Stone Arch Bridge” Structure
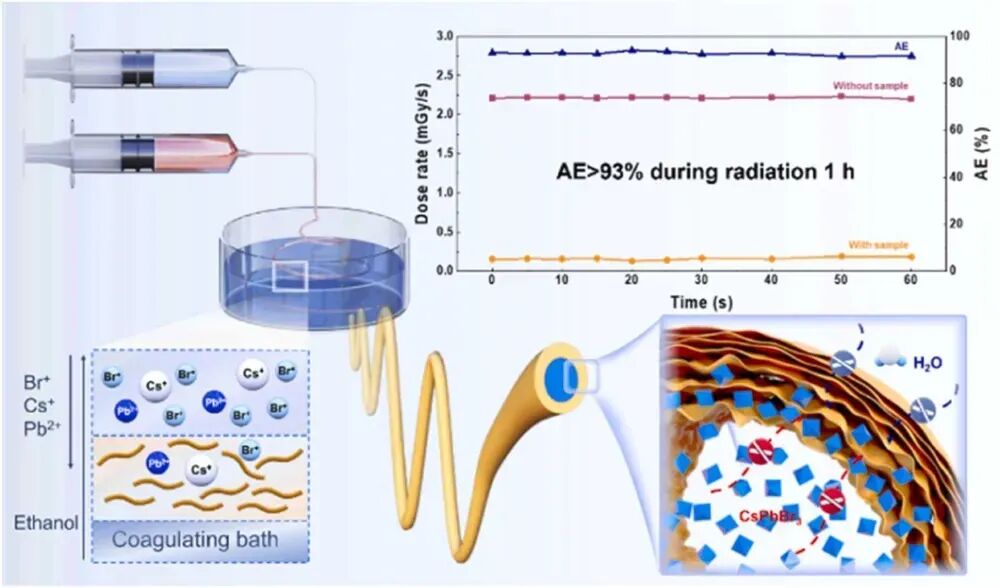
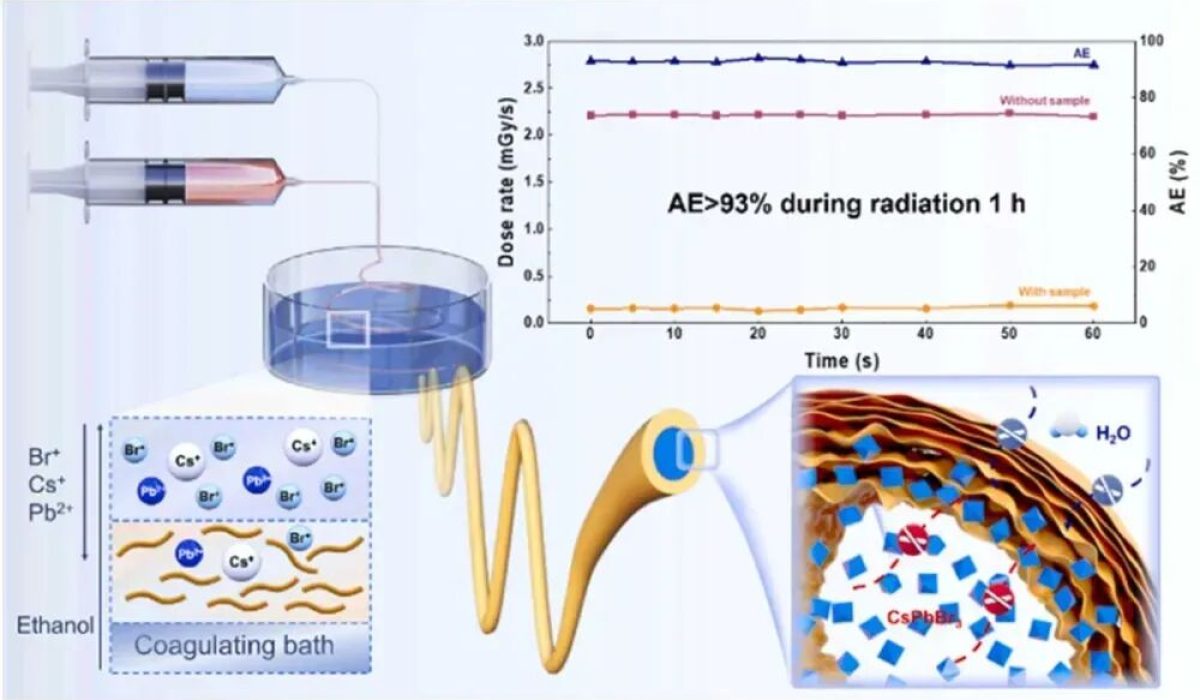
The core advancement lies in the material’s unique architecture. Using a coaxial wet-spinning technique, the team fabricated robust and flexible ANF@CsPbBr3 coaxial fibers. In this design, a tough ANF shell encapsulates a core where CsPbBr3 perovskite crystals are rapidly formed in situ. This method achieves an exceptionally high loading capacity of the X-ray-absorbing filler (CsPbBr3), which is crucial for effective shielding.
The internal crystallization process naturally creates a supportive “stone arch bridge” structure within the fiber, effectively preventing the collapse of the ANF shell. Furthermore, the ANF shell acts as a protective barrier, securely confining the CsPbBr3 core to prevent leakage and blocking external moisture intrusion, ensuring long-term stability and performance.

Superior Integrated Performance for Practical Application
This ANF@CsPbBr3 coaxial fiber demonstrates excellent processability and can be manufactured into shielding paper using conventional paper-making techniques. The resulting material exhibits an outstanding combination of properties:
- High Shielding Efficiency: Achieves over 93% X-ray attenuation across the 20-70 kV range.
- Lightweight & Strong: Possesses a low density of 1.01 g/cm³ and a robust tensile strength of 11.8 MPa.
- Excellent Flexibility & Flame Resistance: The ANF matrix provides remarkable bendability and inherent flame-retardant properties.
- Low Secondary Radiation: Minimizes harmful secondary scatter, enhancing safety.
- Complementary Absorption: The combination of high-Z elements Cesium (Cs) and Lead (Pb) offers complementary absorption edges, effectively covering blind spots that single elements like Pb have.
Addressing Industry Challenges
Traditional X-ray shielding relies heavily on dense, inflexible, and often toxic materials like lead or tungsten alloys. While polymer composites containing high-Z fillers offer more flexibility, they typically struggle with low filler loading, leading to poor shielding or material degradation (e.g., chalking, peeling).
This new ANF@CsPbBr3 coaxial fiber-based material directly addresses these limitations. The core-shell structure allows for maximal filler loading without compromising mechanical integrity or flexibility. The successful integration of stable, high-performance perovskite into a durable polymer fiber paves the way for scalable production of next-generation personal protective equipment, medical apparel, and flexible shielding for sensitive electronics.
Research Background & Publication
This significant work, titled “In-situ synthesis of flexible aramid nanofiber@CsPbBr3 coaxial fiber-based paper for effective X-ray shielding,” was published online in the prestigious journal Nano Today on May 7, 2025. The research was jointly communicated by Professor Zhiwen Jin from Lanzhou University, and Professors Jingru Zhang and Zhaoqing Lu from Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, marking a major step forward in the development of advanced radiation protection materials.