Summary:This paper summarizes the performance, modification research, dyeing and printing performance research and development status of aramid fiber, as well as the application and research of aramid fiber in metallization, sports, flexible stab-proof and bulletproof materials, aerospace materials, etc.
The full name of aramid fiber is aromatic polyamide fiber (aramid). It is a fiber composed of linear macromolecules composed of aromatic groups connected by imide bonds or amide bonds. At least one of them is directly connected to two aromatic rings. 85% of imide bonds or amide bonds, and when imide bonds exist, their value does not exceed the number of amide bonds. Aramid fiber has excellent flame retardancy, heat resistance, high toughness, high modulus and excellent insulation ability. It is a high-performance fiber. After years of research and development, aramid fiber has been commercialized and used in the military industry. National defense, aerospace, transportation, energy communications, environmentally friendly building materials, protective equipment, sports equipment, paper manufacturing and other fields. Although my country’s aramid companies are still unable to compete with Teijin and DuPont due to technological blockades, through continuous research by domestic technical personnel, China has achieved localization of all para-aramid specifications and varieties, including high-modulus and high-strength para-aramid. In 2020, China will achieve an annual output of 29,000 tons of aramid fiber, mainly based on the two most classic products – meta-aramid fiber (PMIA) (market share 80%) and para-aramid fiber (PPTA). At the same time A breakthrough in the preparation technology of ultra-high-strength para-aramid fiber that can be used in military bulletproof helmets. The backbone enterprises of kiloton-level para-aramid in my country mainly include Tayho New Materials (of which meta-aramid ranks second in the world), Sinochem International, SINOARA, Blue Star New Materials, Yizheng Chemical Fiber, and Ruisheng New Materials. Aramid fiber is one of the important varieties of China’s key strategic materials.
1. Structure and properties of aramid fiber
1.1 The structure of aramid fiber
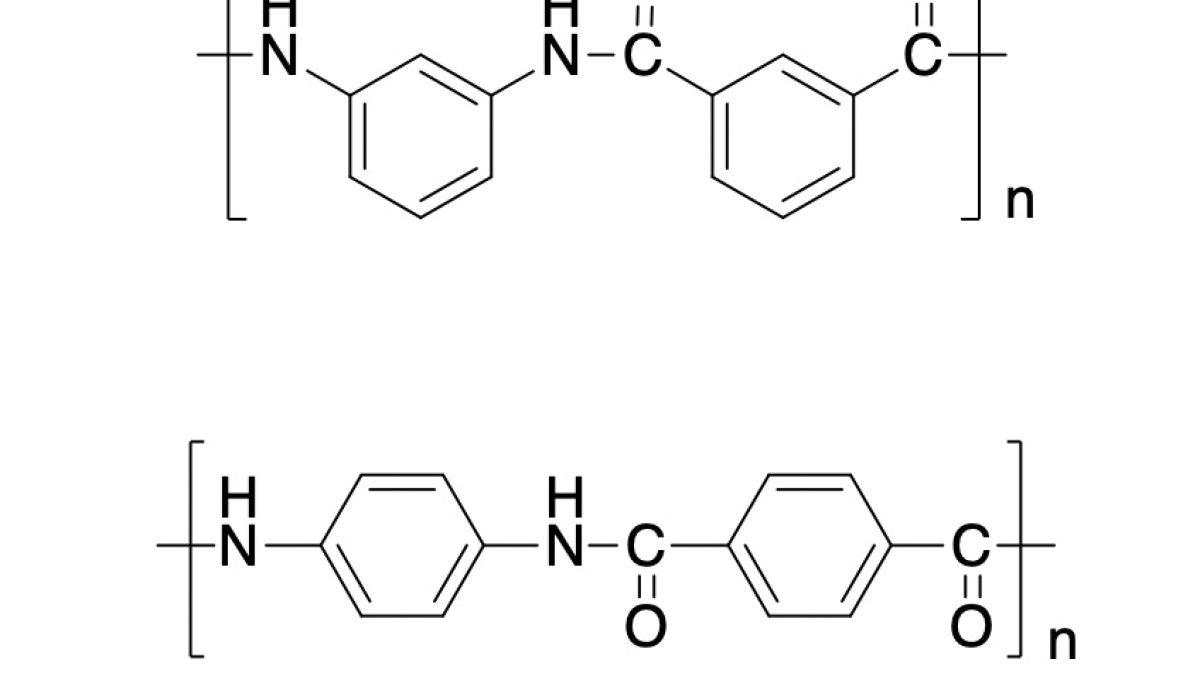
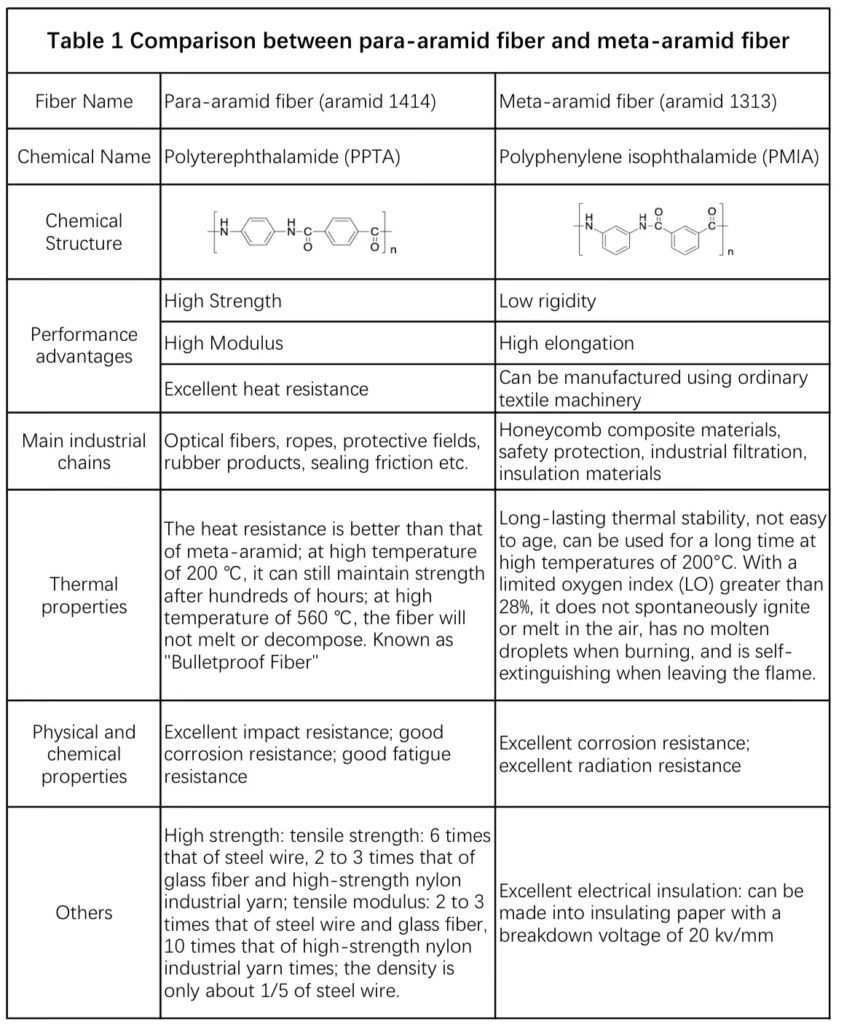
The structure, synthesis method and advantageous performance comparison of two common aramid fibers are shown in Table 1.
During spinning, the main chain has such a large conjugated benzene ring, a regular linear rigid structure, and a highly ordered molecular chain. Even in a limited space, the molecular chain of aramid fiber can carry out high-density spinning along the orientation of the fiber. , multi-layer stacking to form a highly oriented, high-strength structure, and there are hydrogen bond cross-links between the molecular chains of aramid fiber, that is, the carbonyl group of one molecular chain can form a hydrogen bond with the hydrogen of the amide group of another molecular chain. Microfiber structure, sub-crystalline structure and skin-core structure are all supramolecular structural forms of aramid fiber. For the skin-core structure, the crystallinity of the skin layer is small (thickness 0.1 μm ~ 1 μm) and the degree of orientation is high (the core layer is single crystal arranged along the fiber axis). The longitudinal molecular orientation is almost parallel to the orientation of the fiber axis, and the axial direction has strong covalent bonds. When the axial force is broken, the structure will split into finer microfiber monofilaments; the transverse direction is the radiation with hydrogen bonding sheets. When a force perpendicular to the axial direction is exerted on the fiber, the force point is delaminated and destroyed. The aramid fiber has anisotropic mechanical properties due to its strong and weak axis and weak longitudinal and transverse strength, and its poor compression and shear properties. Even so, the compressive strength is higher than that of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene due to the presence of lateral hydrogen bonds in aramid fibers.
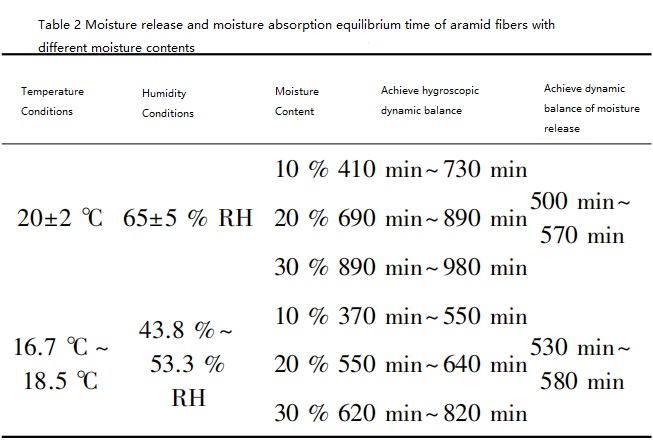
Zhang Yaru observed through a scanning microscope that the meta-aramid fibers of three brands, Longbang, Shengqi, and Korea, have relatively smooth longitudinal surfaces. The infrared spectrum showed obvious vibrations of benzene rings and amide bonds, and the orientation degree was 54.2%~ 56.0%, crystallinity 44.5% ~ 54.5%, fiber breaking strength 8.3cN ~ 9.3cN, elongation at break 37.1% ~ 40.3%, initial modulus 40.5cN/dtex ~ 46.6cN/dtex, moisture content under standard atmosphere 7.05 % ~ 7.30%, using pure water and 3.5% sodium chloride to prepare aramid fibers with moisture contents of 10%, 20%, and 30% respectively, the breaking strength decreased by 5.2% ~ 12.7%, 16.0% ~ 21.8%, 21.2% ~ 28.5%. The elongation at break increases with the increase in moisture content. The moisture content increases the most at 2.2% ~ 4.6%. The initial modulus decreases by 5.1% ~ 25.0%, 26.1% ~ 35.3%, and 29.8 respectively. %~50.0%, there is little difference in tensile properties between the two media. Under various conditions, the moisture release and moisture absorption equilibrium times of aramid fibers with different moisture contents are shown in Table 2 below.
Thermal degradation of para-aramid fibers follows second-order reaction kinetics. Yang Chen and others used high-temperature baking of para-aramid and found that the molecular structure and mechanical and thermal properties of para-aramid remained stable below 350°C. After exceeding 350°C, as the temperature increases, the molecular structure of the fiber decreases. Cracking and cross-linking gradually begin to occur, and the mechanical and thermal properties gradually decrease. When the temperature reaches above 450°C, the crystallinity and orientation of the fiber decrease, and the intrinsic viscosity in each direction and the apparent grain size of the crystal plane decrease to varying degrees increase.
1.2 Synthesis of aramid fiber
1.3 Properties of aramid fiber
2. Modification of aramid fiber
2.1 Physical etching modification
2.2 Chemical etching modification of aramid fibers
2.3 Chemical graft modification
2.4 Spinning modification
3. Research on dyeing and printing of aramid fiber The color of aramid fiber is mainly dyed by carrier, non-water medium
3.1 Dyeing of meta-aramid fiber
3.1.1 Carrier staining
3.1.2 Surface modification dyeing
3.1.3 Solvent dyeing
3.2 Dyeing of para-aramid fiber
3.3 Printing of aramid fabrics
4. Applications of aramid fiber
4.1 Metallization applications
4.2 Applications in sports
4.3 Application of flexible stab-proof materials and bullet-proof materials
4.4 Aerospace applications
4.5 Other applications
5. Prospects for Aramid Fibers
This asset is the most comprehensive knowledge on aramid fiber, if you want full version pls contact Mr. Ken. His wechat and whatsapp is listed below


His Email address is ken@hipfiber.com
MP number is +86-17749777593